NeuralByte's weekly AI rundown - 28th January
Discover Lumiere, Morpheus-1 lucid dream inducing AI model, Harvard's robotic hope, and more in the world of AI breakthroughs.
Greetings fellow AI enthusiasts!
This week in the ever-evolving realm of artificial intelligence has been nothing short of big news. Let's dive into the exciting developments that have surfaced recently.
🧠 Stay curious!
Dear subscribers,
Thanks for reading my newsletter and supporting my work. I have more AI content to share with you soon. Everything is free for now, but if you like my work, please consider becoming a paid subscriber. This will help me create more and better content for you.
Now, let's dive into the AI rundown to keep you in the loop on the latest happenings:
🌐 Google unveils Lumiere: A new model for realistic AI video generation
🦾 Microsoft is forming a team to develop more cost-effective generative AI
💻 New MIT CSAIL study suggests that AI won’t steal as many jobs as expected
🦿 Harvard’s robotic exoskeleton: A new hope for Parkinson’s patients
🎨 Kin.art: A new defense for artists against AI scraping
🧑💻 Stability AI introduced Stable Code 3B
💭 AI inducing lucid dreams: The Morpheus-1 model
🕸️ Google Chrome introduced new generative AI features
✈️ AI-Enabled Valkyrie drone: A glimpse into the future of the US Air Force fleet
✨ Google DeepMind scientists plan to launch AI startup in Paris
🏆 Google’s Gemini Pro surpasses GPT-4 In chatbot arena
And more!
Google unveils Lumiere: A new model for realistic AI video generation
Google, in collaboration with the Weizmann Institute of Science and Tel Aviv University, has proposed Lumiere, a space-time diffusion model aimed at generating realistic videos. The technology, detailed in a recently published paper, is designed to address the growing demand for competent generative AI offerings. Lumiere, which translates to ‘light’, is a video diffusion model that stands out from existing models by synthesizing videos that depict realistic, diverse, and coherent motion, a significant challenge in video synthesis.
The details:
Space-Time U-Net Architecture: Lumiere uses a U-shaped network that processes the video in multiple space-time scales, enabling it to generate the entire temporal duration of the video at once, rather than in segments.
Text-to-Image Diffusion Model: Lumiere leverages a pre-trained text-to-image diffusion model that generates high-quality images from text prompts, and extends it to video generation by adding temporal conditioning.
Content Creation and Editing Tasks: Lumiere can perform various tasks such as text-to-video, image-to-video, video inpainting, cinematography, and stylized generation, using natural language commands and optional reference images.
State-of-the-Art Results: Lumiere outperforms existing methods in terms of motion magnitude, temporal consistency, and overall quality, as evaluated by both quantitative metrics and human judgments.
Why it’s important:
The introduction of Lumiere represents a significant advancement in the field of AI video generation. By addressing the challenge of synthesizing videos that portray realistic, diverse, and coherent motion, Lumiere has the potential to revolutionize the way we create and edit videos. Its ability to generate the entire temporal duration of a video at once, leading to more realistic and coherent motion, sets it apart from existing models. This could have far-reaching implications for industries ranging from entertainment to security, opening up new possibilities for how we use and interact with video content.
Microsoft is forming a team to develop more cost-effective generative AI
Microsoft is reportedly expanding its focus on developing artificial intelligence (AI) technology that requires less computing power and financial resources. The company has formed a new team dedicated to building what it calls “smaller language models” (SLMs), which aim to provide conversational and generative capabilities similar to large language models (LLMs) like OpenAI’s GPT. This initiative could potentially reduce the costs and carbon footprint associated with Microsoft’s AI products and services.
The details:
Microsoft’s new team, known as the GenAI team, is expected to be incorporated into Microsoft’s Azure cloud unit.
The GenAI team aims to create AI that matches or exceeds the functionality of models sourced from companies like OpenAI while optimizing for smaller sizes.
Microsoft has relocated several top developers from its research group to support the GenAI team.
Microsoft corporate vice president Misha Bilenko will spearhead the team’s efforts.
Microsoft has incorporated a number of AI capabilities from OpenAI into its offerings.
Why it’s important:
Microsoft’s pursuit of developing smaller and more affordable AI technology could potentially open up new avenues for the company to offer its own solutions, reducing dependence on third-party providers. This initiative represents a significant step towards making AI technology more accessible and sustainable, which could have far-reaching implications for the tech industry and beyond.
New MIT CSAIL study suggests that AI won’t steal as many jobs as expected
A new research study from MIT’s Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory (CSAIL) has attempted to answer the trio of questions: Will AI automate human jobs, and if so, which jobs and when? The study moves beyond what they characterize as “task-based” comparisons and assesses how feasible it is that AI will perform certain roles, and how likely businesses are to replace workers with AI tech.
Contrary to expectations, the MIT researchers found that the majority of jobs previously identified as being at risk of AI displacement aren’t, in fact, “economically beneficial” to automate — at least at present. The key takeaway, says Neil Thompson, a research scientist at MIT CSAIL and a co-author on the study, is that the coming AI disruption might happen slower — and less dramatically — than some commentators are suggesting.
The details:
The study surveyed workers to understand what an AI system would have to accomplish, task-wise, to fully replace their jobs.
The researchers modeled the cost of building an AI system capable of doing all this, and also modeled whether businesses would be willing to pay both the upfront and operating expenses for such a system.
Researchers found that only 23% of the wages paid for doing vision tasks would be economically atractive to automate.
The researchers didn’t investigate the potential impact of text- and image-generating models, like ChatGPT and Midjourney, on workers and the economy.
Why it’s important:
The findings of this study are significant as they provide a more nuanced view of the impact of AI on jobs. While AI has the potential to automate many tasks, the study suggests that it may not be economically viable for businesses to replace workers with AI in many cases. This could mean that the transition to AI-driven workplaces might be slower and less disruptive than previously thought. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for businesses, policymakers, and workers as they navigate the evolving landscape of AI and work.
Harvard’s robotic exoskeleton: A new hope for Parkinson’s patients
Harvard’s Biodesign Lab has developed a robotic exoskeleton that can improve walking and decrease falls in people with Parkinson’s disease. This soft robotic exoskeleton is designed to assist individuals with mobility impairments, focusing on specific issues that impact their ability to move around. For people with Parkinson’s disease, “freezing” is a common problem that affects their ability to walk and increases the likelihood of falls. The new technology features sensors that detect movement and use algorithms to estimate the walker’s gait.
The details:
The wearable technology uses cable-driven actuators that assist walking midstride.
The research was carried out over six months with a 73-year-old man with Parkinson’s who experiences freezing more than 10 times a day.
The team was able to eliminate freezing in patients while walking indoors and only occasional episodes outdoors.
The same group previously designed an exosuit for stroke patients.
Why it’s important:
This development is significant as it addresses a critical issue faced by individuals with Parkinson’s disease. The ability to walk without freezing can greatly improve the quality of life for these individuals. Furthermore, the use of such technology could potentially reduce the need for medication or surgery, which are currently the primary methods of managing Parkinson’s symptoms. This innovation from Harvard’s Biodesign Lab represents a promising step towards harnessing the power of robotics and AI to improve healthcare outcomes.
Kin.art: A new defense for artists against AI scraping
Kin.art, a new online art hosting platform, has launched a tool that promises to defend artists’ entire portfolios from AI scraping. This tool is part of the platform itself and provides built-in defenses against AI whenever an artist uploads one or more of their images to its servers. The tool uses a unique machine learning technique and promises to be much faster than its rivals, applying the defense to a given image in only milliseconds.
The details:
Kin.art’s tool is designed to prevent artwork from being included in a dataset used to train AI models.
The tool uses image segmentation, a machine learning technique, to “scramble” the image for algorithms that may wish to scrape it.
The scrambled image appears disordered to a machine’s eye but looks the same as the artist intended to the human eye.
If the image is downloaded or saved without authorization, it will appear to have an additional layer of scrambling.
Kin.art’s tool was co-developed by Flor Ronsmans De Vry, who co-founded Kin.art, an art commissions management platform.
The tool does not require cryptographically modifying images, which can be expensive.
It can also be combined with other methods as additional protection.
Why it’s important:
The launch of Kin.art’s tool is a significant development in the field of AI and art. As generative AI models become more prevalent and sophisticated, the risk of artwork being used without the artist’s knowledge or permission increases. By providing a fast and effective way to protect artwork from being included in AI training datasets, Kin.art is helping to ensure that artists’ rights are respected in the era of AI.
Stability AI introduced Stable Code 3B
Stability AI, a company renowned for its stable diffusion text-to-image generative AI technology, has announced the release of its first new AI model of 2024: the commercially licensed Stable Code 3B. This 3-billion parameter model is designed to provide code completion capabilities for software development. Despite its compact size, Stable Code 3B can run locally on laptops without dedicated GPUs, offering competitive performance against larger models like Meta’s CodeLLaMA 7B.
The details:
Stable Code 3B is not just capable of suggesting new lines of code, but it can also fill in larger missing sections in existing code.
The model has an advanced code completion capability known as Fill in the Middle (FIM).
The training for the model was optimized with an expanded context size using a technique known as Rotary Position Embeddings (RoPE), allowing context length up to 100k tokens.
Stable Code 3B is built on Stability AI’s Stable LM 3B natural language model.
The model was trained on code repositories, programmer forums, and other technical sources.
It covers popular languages like Python, Java, JavaScript, Go, Ruby, and C++.
Early benchmarks indicate it matches or exceeds the completion quality of models over twice its size.
Why it’s important:
The introduction of Stable Code 3B represents a significant advancement in the field of AI-powered code generation. By offering a compact yet powerful model, Stability AI is making strides in making AI-powered code generation more accessible and efficient. This could potentially revolutionize the way software development is approached, making it easier for developers to write and complete code. Furthermore, the model’s ability to fill in missing sections of code could prove invaluable in large projects where such gaps can lead to significant issues.
AI inducing lucid dreams: The Morpheus-1 model
Named after the greek god of dreams Morpheus-1 is AI model capable of inducing lucid dreams. This model uses the same underlying transformer technology that powers ChatGPT and MidJourney, but with a unique twist: it takes brain activity as the prompt and generates shaped sound waves that can react with that brain state as an output. This new approach to brain stimulation will be tied to a new headband product called The Halo that Prophetic is releasing as a beta program.
The details:
The Morpheus-1 model was trained on 8 GPUs over two days.
Unlike large language models or image generators, Morpheus-1 takes brain activity as the prompt.
It generates shaped sound waves that can react with the current brain state.
The Halo, a new headband product, will send these sound waves, or ultrasound holograms, into the brain.
These ultrasound holograms connect with the current brain state and can put the mind into a lucid state.
Why it’s important:
The implications of this technology are vast. By inducing a lucid dream state, it could potentially open up new avenues for exploring the human mind and consciousness. This could be particularly beneficial for therapeutic applications, such as treating PTSD or other mental health conditions. Furthermore, the use of AI in this context underscores the versatility and potential of AI applications in various fields. As we continue to understand and harness the power of AI, we can expect to see even more innovative uses of this technology in the future.
Google Chrome introduced new generative AI features
Google Chrome is introducing three new generative AI features to enhance user experience. These features, which are part of the latest release of Chrome (M121), aim to make browsing more efficient and personalized. Users can try out these features on Macs and Windows PCs in the U.S. by signing into Chrome, selecting “Settings” from the three-dot menu, and navigating to the “Experimental AI” page.
The details:
Tab Organizer: This feature allows Chrome to automatically suggest and create tab groups based on your open tabs, making it easier to manage multiple tasks.
Custom Themes with AI: Building on generative AI wallpapers introduced with Android 14 and Pixel 8 devices, this feature allows users to quickly generate custom themes based on a subject, mood, visual style, and color of their choice.
Writing Help: This feature aims to make writing on the web less daunting, especially in public spaces or forums. You’ll be able to summon this feature by right clicking on the text field and selecting “Help me write”.
Why it’s important:
The integration of the latest machine learning and AI technologies into Chrome represents a significant step towards making web browsing easier, safer, and more accessible. These new features not only improve practical, everyday tasks but also personalize the user experience. As these features continue to evolve, they have the potential to transform how we interact with the web.
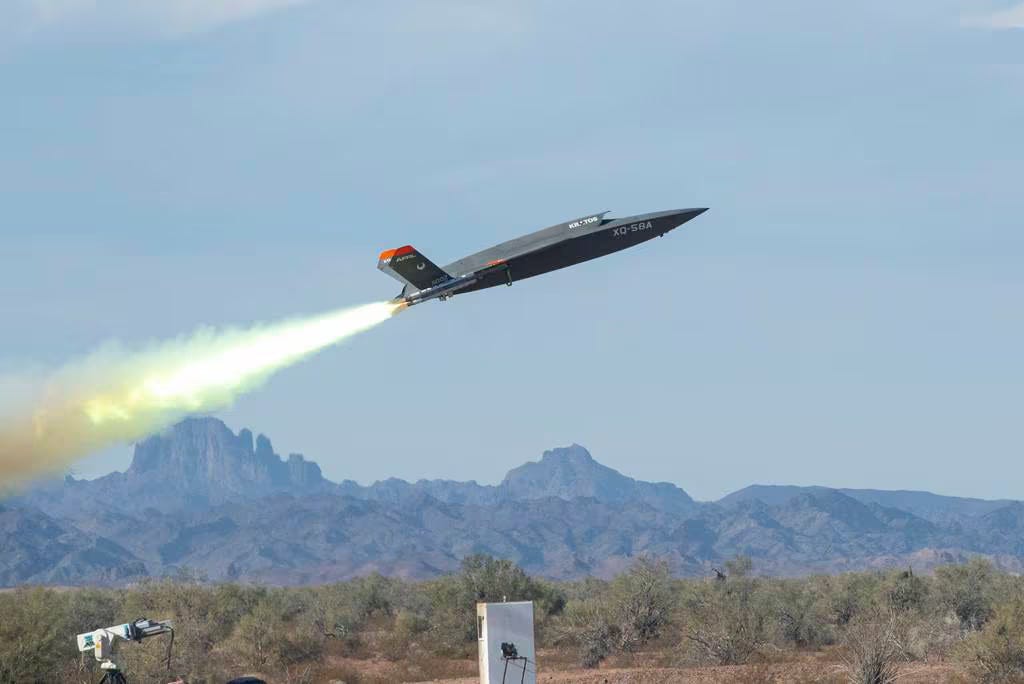
AI-Enabled Valkyrie drone: A glimpse into the future of the US Air Force fleet
The U.S. Air Force is testing sophisticated software aboard an XQ-58A Valkyrie drone, a development that will shape the future of autonomous technology deployment in the military. The drone, manufactured by Kratos, completed a three-hour sortie near Eglin Air Force Base, Florida, in July, marking the first time it relied on artificial intelligence algorithms.
The software was refined over millions of hours in simulation and digital environments, including flights with an experimental F-16 jet known as the X-62 VISTA. The Valkyrie drone has proven to be an excellent test bed, capable of revealing innovative approaches to traditional tasks.
Details
The Valkyrie drone’s AI programming was matured over millions of hours in simulation and digital environments.
The drone flew a three-hour sortie near Eglin Air Force Base, Florida, relying for the first time on artificial intelligence algorithms.
The Valkyrie builds upon years of the Air Force’s Skyborg program and is closely linked to its more recent effort for collaborative combat aircraft, or CCA.
The service plans to pair human pilots with CCAs to afford greater flexibility and firepower.
The uncrewed aircraft could execute a variety of assignments: conducting reconnaissance, gathering intelligence, jamming signals, serving as decoys, and striking targets with their own missiles.
Officials have said CCAs could range in cost and complexity, with some being expensive and precious while others could be easily sacrificed in combat.
Why it’s important:
The testing of AI-enabled Valkyrie drone signifies a significant shift in military operations. The integration of AI in military drones allows for more efficient and effective execution of tasks, potentially reducing human risk in combat situations. The success of this technology could pave the way for a new era of autonomous warfare, where AI plays a crucial role in decision-making processes.
Google DeepMind scientists plan to launch AI startup in Paris
Two scientists from Google DeepMind, the artificial intelligence division of Alphabet Inc., are in talks with investors about forming an AI startup in Paris, according to sources familiar with the conversations. The team, led by Laurent Sifre and Karl Tuyls, has discussed a financing round that may exceed €200 million ($220 million), a large sum for the field of AI. The venture, currently known as Holistic, may be focused on building a new AI model. Sifre and Tuyls are both renowned experts in their field, having worked on groundbreaking research such as the Go game and multi-agent reinforcement learning. Their departure from DeepMind is a sign of the strong investor interest and talent pool in the French AI ecosystem, which has seen several high-profile startups and research labs emerge in recent years.
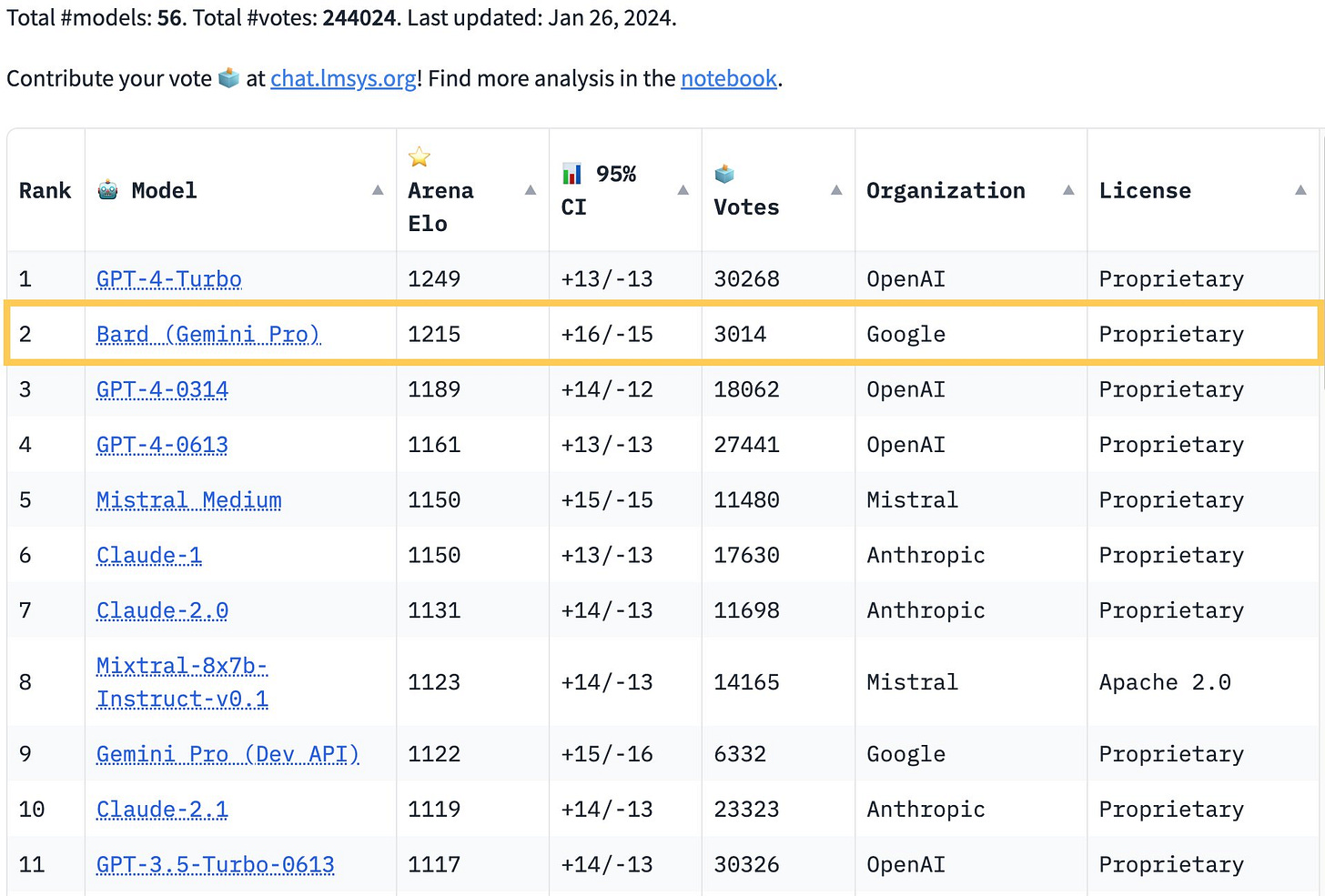
Google’s Gemini Pro surpasses GPT-4 In chatbot arena
Google has achieved a remarkable feat by ranking second on the HuggingFace Chat Bot Arena Leaderboard, beating OpenAI’s GPT-4 with its Bard model. Bard is part of Google’s Gemini project, which aims to create the most advanced natural language generation system. The article discusses the implications of this achievement for the future of generative AI, as well as the competition among the leading players in the field. It also mentions some of the latest developments and features of Google, OpenAI, and Meta, such as the “Help me Write” feature in Google Chrome, the GPT-4 Turbo preview model, and the upcoming Llama 3 model.
Quick news
NVIDIA RTX AI transforms standard video into stunning HDR visuals (link)
Google termination of Appen contract exposes precarious conditions for AI 'ghost workers,' according to union reports (link)
Elevenlabs Introduces Dubbing Studio for Full Control Over Transcript, Translation, Timing, and More (link)
AI systems that monitor emotions are banned in the EU (link)
New Possibilities for Unity Developers: Seamless Integration of Advanced AI Models in Games with Hugging Face Hub (link)
Google recently announced internally its corporate goals for 2024 (link)
SAP unveils $2.2 billion restructuring plan in 2024, focusing on AI-centric business growth, impacting 8,000 positions (link)
Apple's Car project targets 2028 launch with a focus on level 2+ autonomy, primarily for highways (link)
Amazon unveils Alexa Plus: A new frontier in generative AI, introducing monthly subscription for enhanced capabilities (link)
Techsomed's BioTraceIO boosts precision in liver treatments with advanced patient safety features. (link)
Smarter iPhone experience with apple's iOS 17.4. enhanced Siri and messages with AI-powered features, powered by ChatGPT (link)
For daily news from the AI and Tech world follow me on:
Be better with AI
In this section, we will provide you with comprehensive tutorials, practical tips, ingenious tricks, and insightful strategies for effectively employing a diverse range of AI tools.
How to experience Meta's AudioBox using your own voice
Visit the AudioBox demo (for U.S. users, consider using a VPN or a VPN-enabled browser like Arc for access) and select 'Try demos.'
Opt for "Your Voice" to utilize your audio sample, or opt for text descriptions or pre-loaded voices as alternatives.
Select 'Record your voice.' AudioBox will guide you to read a brief sentence to upload your vocals to the model.
Upon completion of the recording (or using a pre-existing sample recording), input the text you wish to generate. AudioBox will then produce two recordings mimicking your vocal style!
It doesn’t sound much like me but I recorded it with my laptop mic so maybe yours will be better.
Tools
🗣️ Talently.ai - Experience the future of hiring with Conversational AI Interviews. (link)
🖼️ Blockade Labs - Amazing tool for generating skyboxes for games (link)
📸 Keep it shot - Swiftly rename and locate disorganized screenshots using AI. (link)
🎙️ Norm AI - Address compliance risks at scale with AI. (link)
🎨 Recraft - Craft and modify graphics with a consistent brand aesthetic. (link)
👨💻 brikly - Source top engineers efficiently on our platform. (link)
👨💼 KPI Builder - Discover the key performance indicators (KPIs) critical for founders to prioritize. (link)
We hope you enjoy this newsletter!
Please feel free to share it with your friends and colleagues and follow me on socials.